A cross-site scripting (XSS) Zimbra security vulnerability is actively exploited in attacks targeting European media and government organizations. Zimbra is an email and collaboration platform that also includes instant messaging, contacts, video conferencing, file sharing, and cloud storage capabilities.
A threat actor, likely Chinese in origin, is actively attempting to exploit a zero-day vulnerability in the Zimbra open-source email platform as part of spear-phishing campaigns that commenced in December 2021.
The espionage operation — codenamed "EmailThief" — was detailed by cybersecurity company Volexity in a technical report published Thursday, noting that successful exploitation of the cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability could result in the execution of arbitrary JavaScript code in the context of the user's Zimbra session.
Volexity attributed the intrusions, which started on December 14, 2021, to a previously undocumented hacking group it's tracking under the moniker TEMP_HERETIC, with the assaults aimed at European government and media entities. The zero-day bug impacts the most recent open-source edition of Zimbra running version 8.8.15.
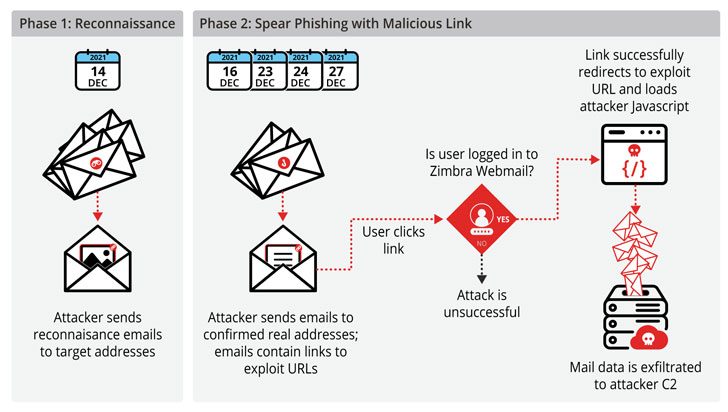
The attacks are believed to have occurred in two phases; the first stage aimed at reconnaissance and distributing emails designed to keep tabs if a target received and opened the messages. In the subsequent stage, multiple waves of email messages were broadcasted to trick the recipients into clicking a malicious link.
The unpatched flaw, should it be weaponized, could be abused to exfiltrate cookies to allow persistent access to a mailbox, send phishing messages from the compromised email account to widen the infection, and even facilitate the download of additional malware.
Users of Zimbra should consider upgrading to version 9.0.0, as there is currently no secure version of 8.8.15 according to the company.

